


Introduction of Micro Heat Pipe
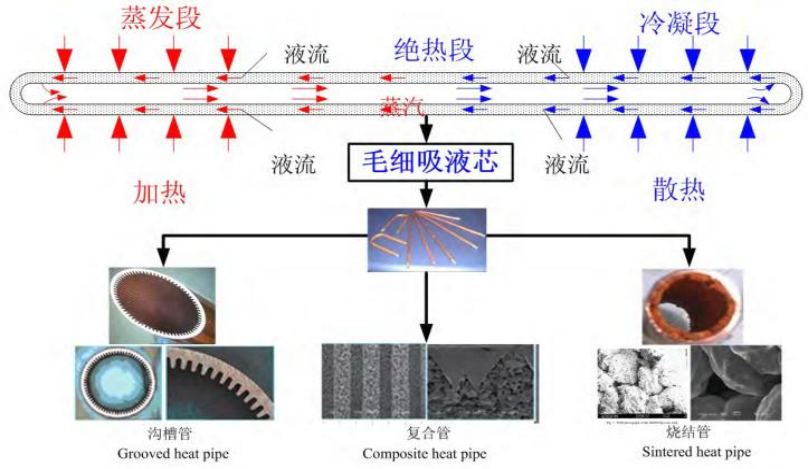
As shown in the diagram of heat transfer principle of heat pipe, one end of the heat pipe is evaporation zone (heat in) and the other end is condensation zone (heat out). When the evaporation zone is heated, liquid working-fluid in capillary wick is vaporized, the vapor flows to the condensation zone driven by the pressure difference between the hot evaporation zone and the cold condensation zone and then condensates in the condensation zone. The working-fluid, which is transformed into liquid, flows from the condensation zone to the evaporation zone along the capillary structure driven by the capillary pressure. In a cycle like this, heat is transferred from one end to the other of the heat pipes.
Different applied environment and working conditions requires different micro heat pipe with a different structure and heat transfer performance. The heat transfer performance of micro heat pipes relies heavily on the capillary wick structure in the inner surface, so design and manufacturing technology of the wick structure is the key and critical factor in the production process of the micro heat pipe at all time.
According to different wick structure, micro heat pipe includes three types: grooved heat pipe, sintered heat pipe and composite heat pipe.
微型熱管介紹
如同熱管的熱傳遞原理圖所示,熱管的一端為蒸發區(吸收熱量),另一端為冷凝區(釋放熱量)。當蒸發區受到加熱時,毛細結構中的液態工質被汽化,蒸汽在蒸發區與冷凝區之間的壓差驅動下流向冷凝區,並在冷凝區冷凝為液態。液態工質則沿著毛細結構在毛細壓力的作用下,從冷凝區流回蒸發區。如此循環運作,熱量便從熱管的一端傳遞至另一端。
不同的應用環境和工作條件需要不同結構與熱傳性能的微型熱管。而微型熱管的熱傳性能在很大程度上依賴於內壁毛細結構的設計。因此,毛細結構的設計與製造技術始終是微型熱管生產過程中的關鍵因素。
根據毛細結構的不同,微型熱管可以分為三種類型:槽式熱管、燒結式熱管和複合式熱管。
Micro heat pipe structure and working principle
Heat Pipe Products
• Heat Pipe Display
• Straight Heat Pipe
• Flat Heat Pipe
• Special-Shaped Heat Pipe
Heat Pipe Type
Diameter (mm): 1,2,3,4, 5,6,8,10,9.5,12,12.7,16,22
Length(mm): 60~1000
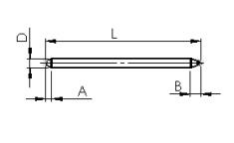
| Diameter(D) | Standard Length(L) | Ineffective Length(A) | Ineffective Length( B) |
| 1±0.05mm | 60~300±1mm | 1~3.0mm | 1~6.0mm、<8mm |
| 2±0.05mm | 60~300±1mm | 1~3.0mm | 1~6.0mm、<8mm |
| 3±0.05mm | 60~300±1mm | 2~5.0mm | 4~7.0mm、< 10mm |
| 4±0.05mm | 60~300±1mm | 2~5.0mm | 4~7.0mm、< 10mm |
| 5±0.05mm | 60~300±1mm | 2~5.0mm | 4~7.0mm、< 10mm |
| 6±0.05mm | 60~2000±1mm | 2~5.0mm | <10mm |
| 8±0.05mm | 60~2000±1mm | 3~5.0mm | <10mm |
| 9.5±0.05mm | 60~600±1mm | <5mm | <14mm |
| 10±0.05mm | 60~600±1mm | <5mm | <14mm |
| 12±0.05mm | 60~600±1mm | <5mm | <15mm |
| 12.7±0.05mm | 60~600±1mm | <8mm | <15mm |
| 16±0.05mm | 60~600±1mm | <8mm | <15mm |
| 22±0.05mm | 60~600±1mm | <8mm | <15mm |
Bending Suggestion
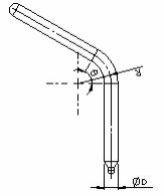
| R and Angle | ||||
| Type | Min. R | Suggestion | Min.Bending Angle | Suggestion |
| Φ3 | 6 | 12 | 180 °> | 180 °> |
| Φ4 | 7 | 16 | ||
| Φ5 | 9 | 20 | ||
| Φ6 | 9 | 24 | ||
| Φ8 | 16 | 32 | ||
| Φ10 | 18 | 40 | ||
| Φ12 | 20 | 48 | ||
Width Table of Flatted Heat Pipe
| Diameter | Thickness | Tolerance | Wide | Tolerance | Diameter | Thickness | Tolerance | Wide | Tolerance |
| Φ3 | 2.5 | ±0.05 | 3.32 | ±0.15 | Φ6 |
3.5 | ±0.05 | 7.6 | ±0.15 |
| 2 | 3.65 | 3 | 7.84 | ||||||
| Φ4 | 3.6 | ±0.05 | 4.3 | ±0.15 | 2.9 | 7.91 | |||
| 3 | 4.68 | 2.5 | 8.13 | ||||||
| 2.5 | 4.95 | 2 | 8.54 | ||||||
| 2.3 | 5.08 | 1.5 | 8.86 | ||||||
| 2.2 | 5.14 | 1.2 | 8.98 | ||||||
| 2 | 5.24 | 1 | 9.05 | ||||||
| Φ5 | 4 | ±0.05 | 5.75 | ±0.15 | Φ8 | 5 | ±0.05 | 9.96 | |
| 3.5 | 6.03 | 4.7 | 10.16 | ||||||
| 3 | 6.29 | 4.5 | 10.2 | ||||||
| 2.5 | 6.54 | 4.2 | 10.45 | ||||||
| 2.3 | 6.66 | 4 | 10.5 | ||||||
| 2 | 6.8 | 3.8 | 10.58 | ||||||
| Φ6 | 5.3 | ±0.05 | 6.62 | ±0.15 | 3.5 | 10.71 | |||
| 5 | 6.82 | 3.2 | 10.9 | ||||||
| 4.8 | 6.92 | 3 | 10.97 | ||||||
| 4.5 | 7.08 | Φ10 和Φ9.5 | 定制 | ||||||
| 4.3 | 7.2 | Φ12 | |||||||
| 4.2 | 7.24 | Φ12.7 | |||||||
| 4 | 7.34 | Φ16 | |||||||
| 3.8 | 7.46 | Φ22 | |||||||
Q-max Test Method For Heat Pipe
Test Method :
1. THeat Source=70±5℃
2. TCondencer =50℃
3. DB=50mm
4. DA=50mm
5. TambieNIT =25±3℃
6. Find the Q-max while T1-T2≤5℃
 |
 |
| Q-MAX |
Thermal Performance Test

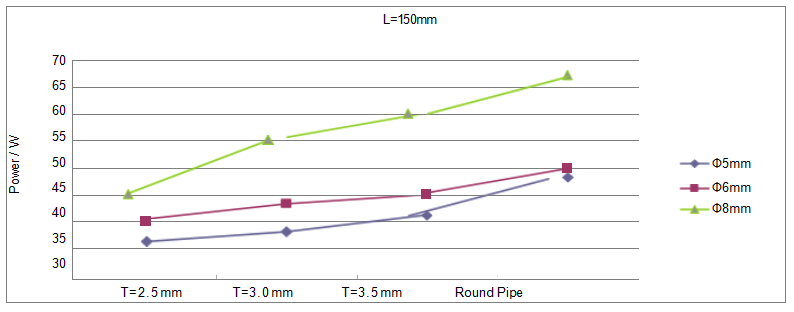
Data Obtained
| Q-max Table (Watt) | ||||||
| Flatten Thickness | Ф5mm | Ф6mm | Ф8mm | |||
| Min. Power | Avg. Power | Min. Power | Avg. Power | Min. Power | Avg. Power | |
| T=2.5mm | 35 | 36 | 38 | 40 | 40 | 45 |
| T=3.0mm | 35 | 38 | 40 | 43 | 52 | 55 |
| T=3.5mm | 40 | 41 | 42 | 45 | 57 | 60 |
| Round Pipe | 45 | 48 | 48 | 50 | 60 | 67 |
(Note: The data comes from the experimental results in 2008)
Thermal Performance Test
type:straight pipe Heat Pipe by L=200mm

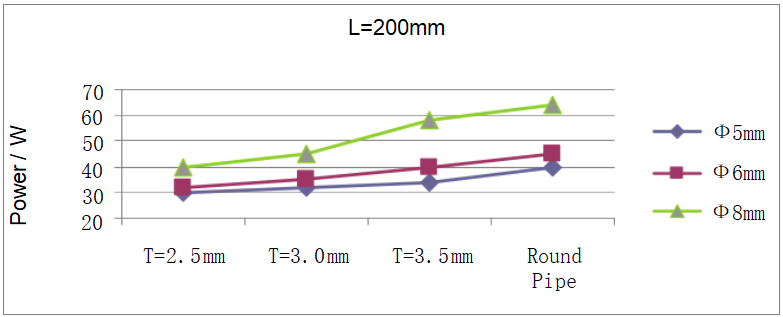
Data Obtained
| Q-max Table (Watt) | ||||||
| Flatten Thickness | Ф5mm | Ф6mm | Ф8mm | |||
| Min. Power | Avg. Power | Min. Power | Avg. Power | Min. Power | Avg. Power | |
| T=2.5mm | 28 | 30 | 30 | 32 | 35 | 40 |
| T=3.0mm | 30 | 32 | 33 | 35 | 40 | 45 |
| T=3.5mm | 33 | 34 | 35 | 40 | 55 | 58 |
| Round Pipe | 35 | 40 | 40 | 45 | 58 | 64 |
(Note: The data comes from the experimental results in 2008)
Thermal Performance Test
type: L pipe Evaporator=50mm
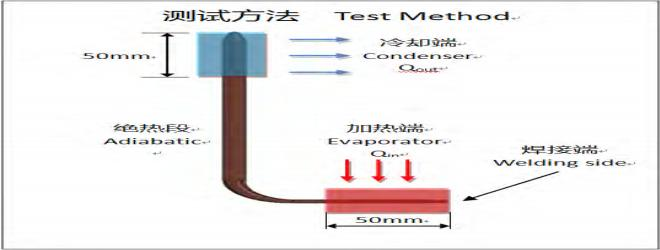
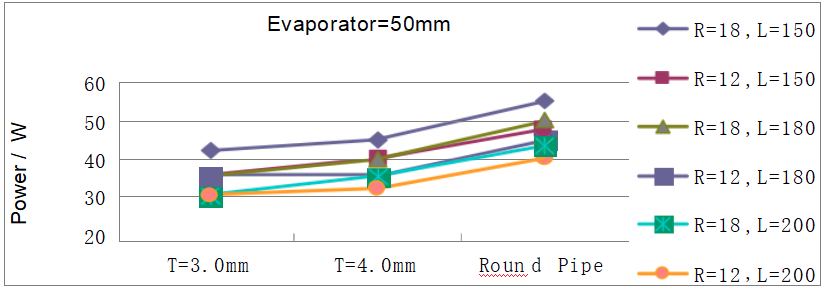
(Note: The data comes from the experimental results in 2008)
Data Obtained
| Q-max Table (Watt) | ||||||||||||
| Specification | Ф6×150 | Ф6×180 | Ф6×200 | |||||||||
| Bending radius | R=18mm | R=12mm | R=18mm | R=12mm | R=18mm | R=12mm | ||||||
| Flatten Thickness | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. |
| T=3.0mm | 40 | 42 | 33 | 35 | 32 | 35 | 32 | 35 | 28 | 30 | 28 | 30 |
| T=4.0mm | 43 | 45 | 38 | 40 | 35 | 40 | 33 | 35 | 32 | 35 | 30 | 32 |
| Round Pipe | 52 | 55 | 45 | 48 | 48 | 50 | 43 | 45 | 40 | 43 | 38 | 40 |
Thermal Performance Test
type:L pipe Evaporator=40mm
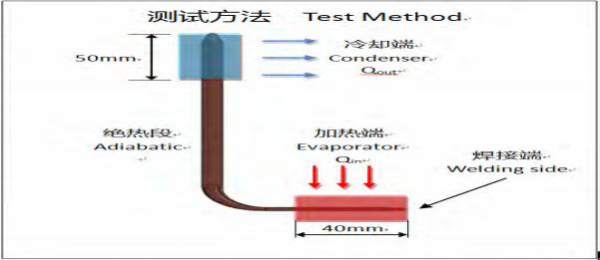
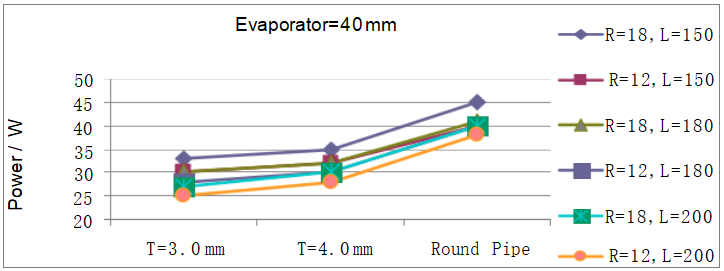
Data Obtained
| Q-max Table (Watt) | ||||||||||||
| Specification | Ф6×150 | Ф6×180 | Ф6×200 | |||||||||
| Bending radius | R=18mm | R=12mm | R=18mm | R=12mm | R=18mm | R=12mm | ||||||
| Flatten Thickness | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. |
| T=3.0mm | 32 | 33 | 29 | 30 | 29 | 30 | 27 | 28 | 25 | 27 | 23 | 25 |
| T=4.0mm | 33 | 35 | 30 | 32 | 30 | 32 | 29 | 30 | 28 | 30 | 26 | 28 |
| Round Pipe | 43 | 45 | 38 | 40 | 40 | 41 | 38 | 40 | 38 | 40 | 36 | 38 |
Thermal Performance Test
type:U pipe Evaporator=50mm
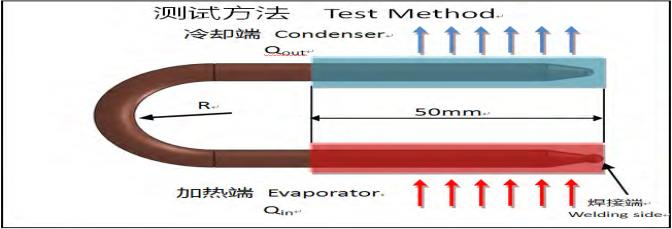
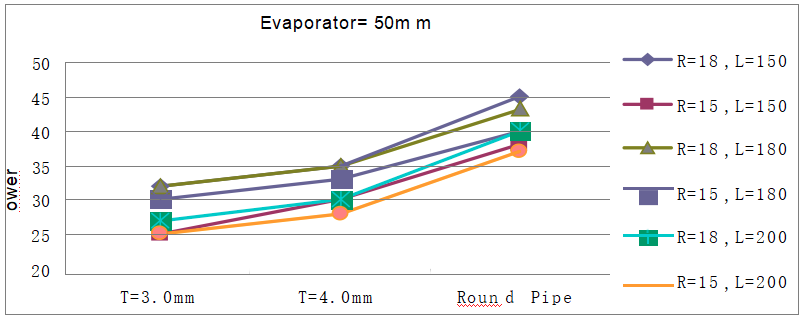
Data Obtained
| Specification | Ф6×150 | Ф6×180 | Ф6×200 | |||||||||
| Bending radius | R=18mm | R=15mm | R=18mm | R=15mm | R=18mm | R=15mm | ||||||
| Flatten Thickness | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. |
| T=3.0mm | 30 | 32 | 23 | 25 | 30 | 32 | 28 | 30 | 26 | 27 | 23 | 25 |
| T=4.0mm | 33 | 35 | 29 | 30 | 33 | 35 | 30 | 33 | 28 | 30 | 27 | 28 |
| Round Pipe | 42 | 45 | 37 | 38 | 40 | 43 | 38 | 40 | 38 | 40 | 35 | 37 |
Thermal Performance Test
type:U pipe Evaporator=40mm
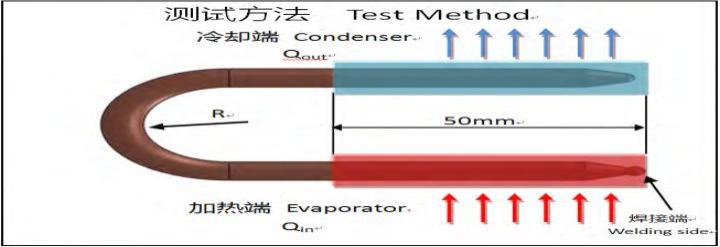
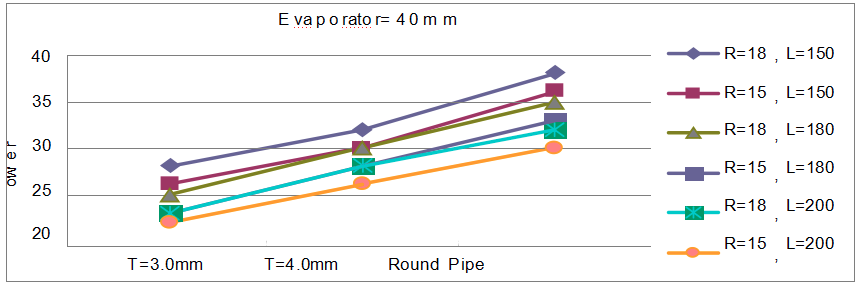
Data Obtained
| Specification | Ф6×150 | Ф6×180 | Ф6×200 | |||||||||
| Bending radius | R=18mm | R=15mm | R=18mm | R=15mm | R=18mm | R=15mm | ||||||
| Flatten Thickness | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. | Min. | Avg. |
| T=3.0mm | 27 | 28 | 25 | 26 | 23 | 25 | 20 | 23 | 21 | 23 | 20 | 22 |
| T=4.0mm | 30 | 32 | 28 | 30 | 29 | 30 | 26 | 28 | 27 | 28 | 24 | 26 |
| Round Pipe | 36 | 38 | 35 | 36 | 34 | 35 | 31 | 33 | 30 | 32 | 28 | 30 |
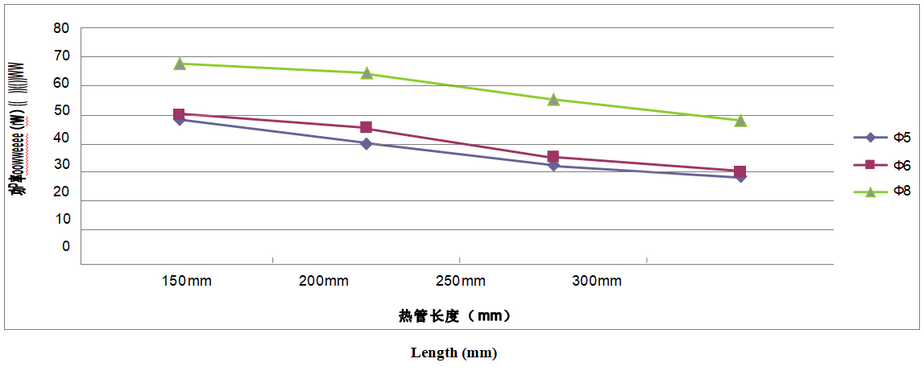
Relationship between power and length(Sintered Heat Pipe)
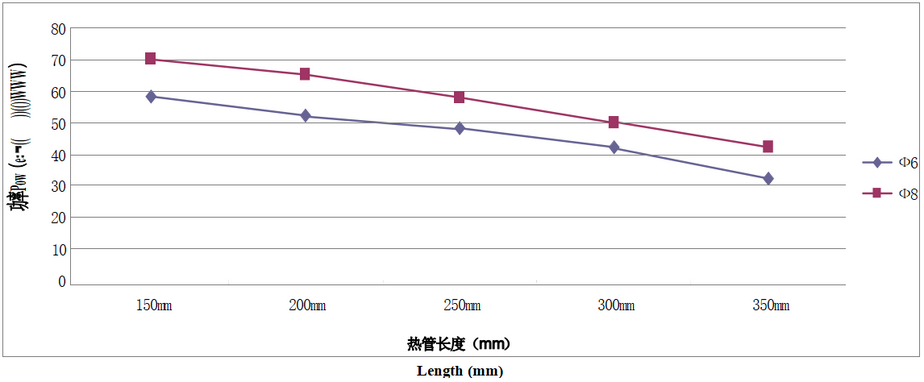
Relationship between power and length(Grooved Heat Pipe)
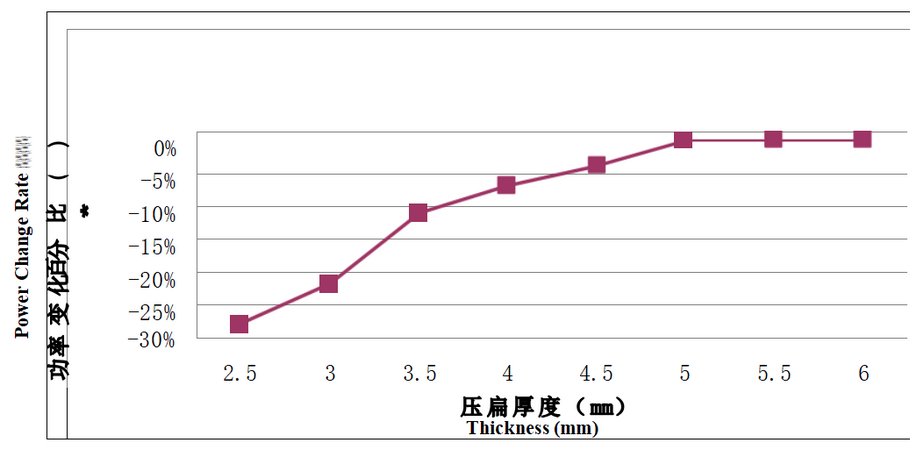
Relationship between power and thickness of heat pipe
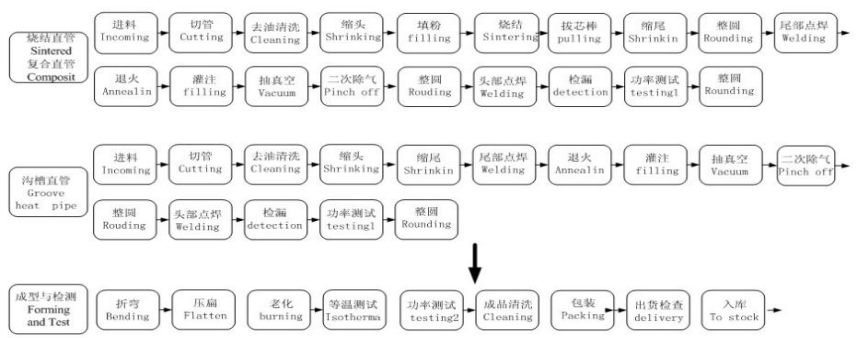
Manufacturing Process of Heat Pipe
Heat Pipe Reliability Test
1.Testing diameter and △T
2.Heating at 150℃ for one hour
3.Testing diameter and △T again
4.Heating at 150℃ for twelve hour again
5.Testing diameter and △T again
Objective:
The purpose of this examination is to test the heat pipe stability which depends on how long the heat would change the shape and performance of the heat pipe in high temperature.

Isothermal test of heat pipe
1. Theat source =70℃±5℃
2. Heating Time T≤15s
3. Check the temperature in upper edge of heat pipe T1
4. Check △T ,△T ≤4℃ , (△T =T-T1)。
Isothermal test of heat pipe
1.Theat source =70℃±5℃
2. Heating Time T≤15s
3. Check the temperature in upper edge of heat pipe T1
4. Check △T ,△T ≤4℃ , (△T =T-T1)。
Objective:
The purpose of this examination is to see the stability of heat pipe, ensuring there are no defective goods after testing.
Thermal Cycle Test of Heat Pipe
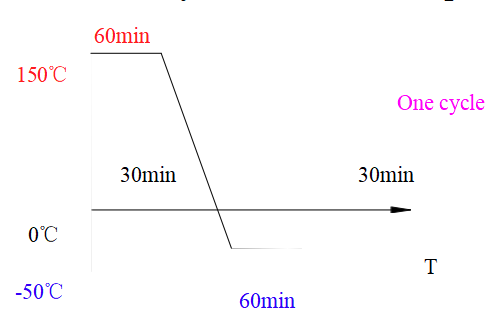
Objective:
From testing ,the useful life and aging rate is revealed.
Our Heat Pipes
Operation Temperature 5~222℃
Burst Temperature(℃) 340℃(备注:增大壁厚可以提高破坏温度)
Useful Life@80℃operation temperature >7年 Years
Heat Pipe Reliability Experiments
1. Useful life Test
2. Leakage Test
3. Performance Test
4.Thermal Cycle Test
5. Salt Spray Test